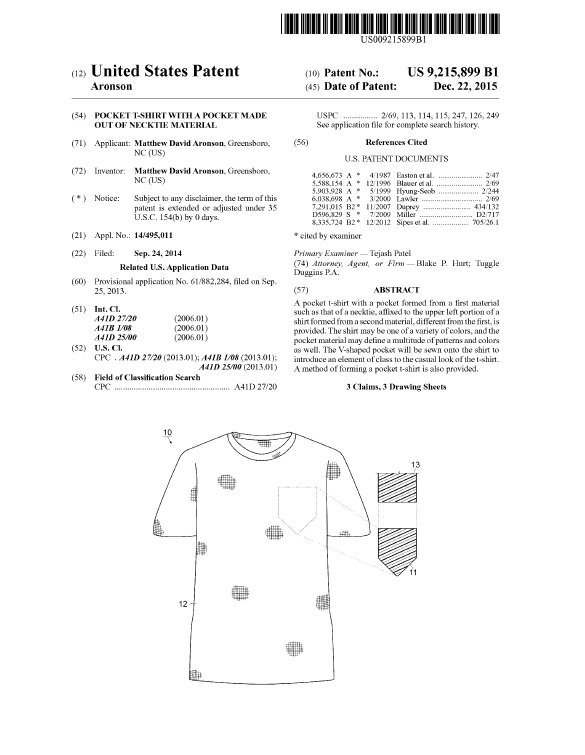
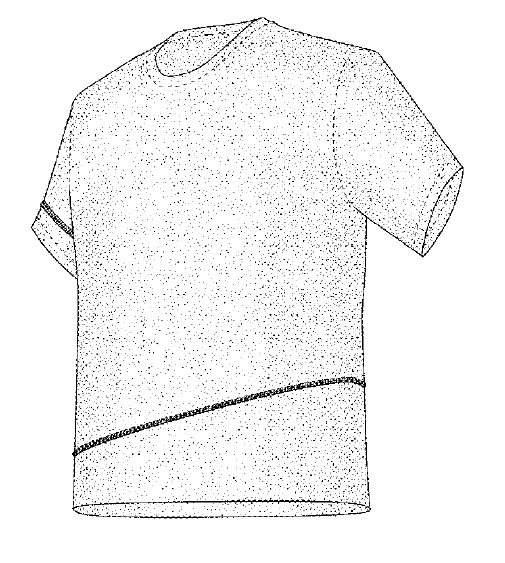
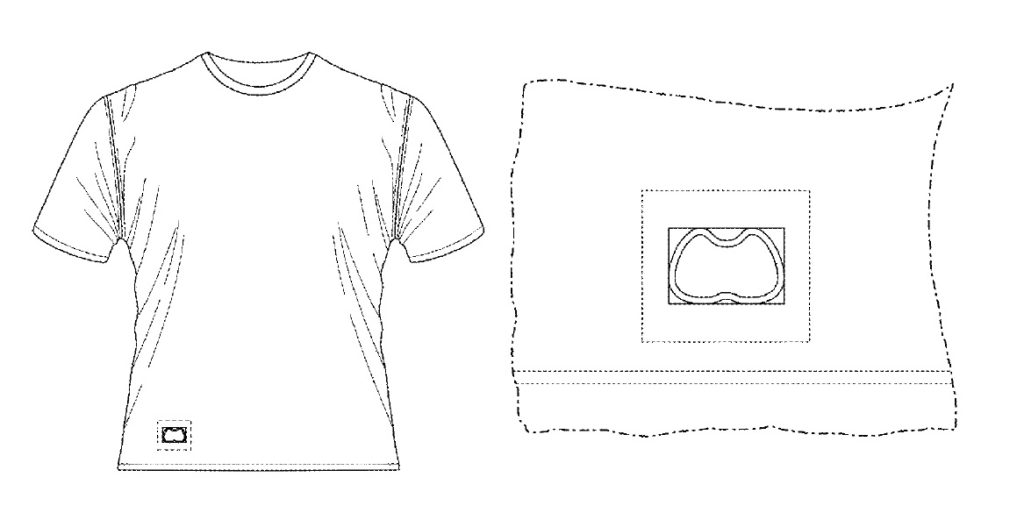
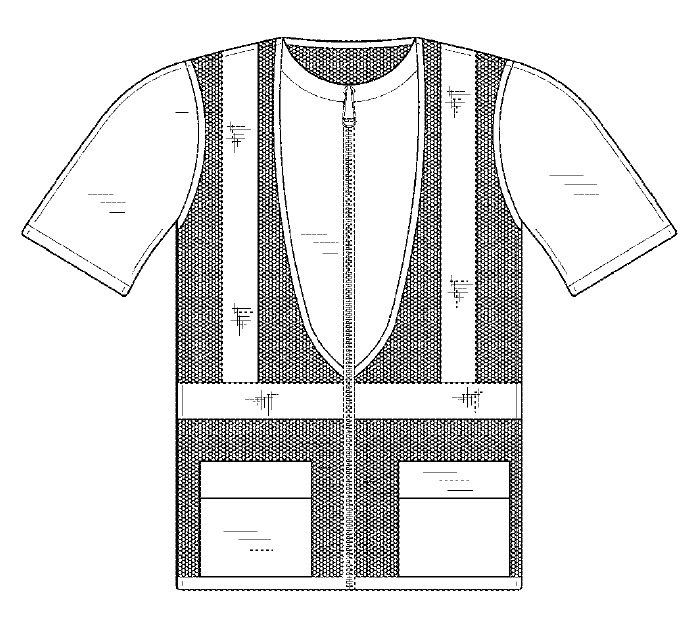
Any moderately successful business most likely has valuable intellectual property that it is may not even be aware it has. A business should, however, be aware of, and inventory, its intellectual property. Why? Several reasons: First, knowing what you have is the first step toward properly protecting it. Second, knowing what you have allows you to document the value of the business when you decide to sell. Second, knowing what you have allows to use the value to attract inventors and obtain financing. Third, knowing what you have allows you to document the value of the business when you decide to sell it.
Where is this intellectual property? It is hidden in the reasons customers continue to deal with the business, and how customers find the goods and services of the business. This checklist can help find it:
- PRODUCT
- Does your product have an overall shape that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have any appearance features that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have a color or color scheme that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have a scent that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have a texture or “feel” that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- PACKAGING
- Does your packaging have an overall shape that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your packaging have any appearance features that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your packaging have a color or color scheme that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your packaging have graphic elements that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your packaging have a scent that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have a texture or “feel” that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- LABELING
- Does your labeling have an overall shape that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your labeling have any appearance features that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your labeling have graphic elements that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your labeling have a color or color scheme that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your product have a texture or “feel” that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- SERVICES
- Does your facility have an overall appearance that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your facility have particular architectural features that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your facility have unique lighting that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your facility have unique signage that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your facility have unique fixtures that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Do you employ unique service items (e.g., bags, cups, napkins) that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Do your employees were uniforms or particular clothing elements that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Do the vehicles that your employees use have an overall appearance that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Do the vehicles that your employees use have unique appearance features that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Do the tools or equipment that your employees use have a distinctive appearance that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- ADVERTISING
- Does your advertising have a theme that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your advertising have a sound or jingle that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your advertising have a color or color scheme that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your advertising have a graphic element that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
- Does your advertising feature a character or mascot that your customers recognize or associate with your business?
Overall, consider how do customers identify your products or services from a distance? Do you or your customers have a nickname for your products or your business? What sticks in the minds of your customers about your products or services? These are thing tie your customers to your business, and are things that you should take steps to protect. Your business definitely has intellectual property, are you doing you best to protect and use it?